InTegriLogic Blog
Imagine a bank locking its doors at night but leaving piles of cash in the open. If someone managed to get inside, they’d have full access with no other barriers. This scenario mirrors traditional cybersecurity practices, where anyone on the network could access everything. Today, a more secure approach called Zero-Trust Security is transforming this outdated model. Let’s explore zero-trust security and the seven key pillars that support it.
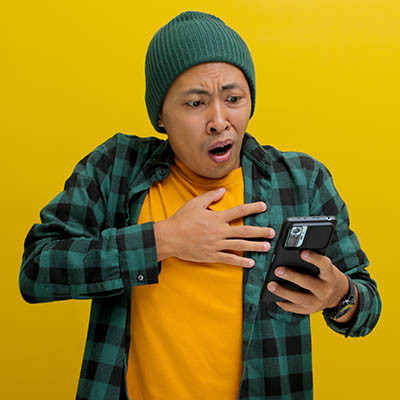
Sextortion scams are alarming. Scammers claim to have hacked into your computer, capturing video footage of you engaging in private, adult activities, as well as the content on your screen. Their threat? Pay up, or they’ll send the footage to all of your contacts.
Recently, these scammers have become even more convincing by including victims' names and pictures of their homes. Let’s break down how these scams work and what you should do if one of these messages lands in your inbox.
Businesses face a wide range of challenges, but some of the most significant issues can come from within the company itself. Whether these problems stem from hackers, disgruntled customers, or unreliable vendors, every business leader has to deal with some form of internal threat. Unfortunately, these threats can sometimes come from the employees themselves. Today, we’ll explore two employee-related issues that can potentially cause major headaches for business owners.
Remote work has proven incredibly useful over the past few years, offering flexibility and efficiency for many businesses. However, with these benefits come significant cybersecurity challenges that must not be overlooked. If your business utilizes remote operations and you aren’t concerned about cybersecurity, it’s time to rethink your approach.
While no one would suggest cutting back on cybersecurity, it's important to recognize that overinvesting and overreaching can lead to its own set of problems. This issue, known as cybersecurity sprawl, can have serious consequences for your business if not properly managed. Let’s explore how to avoid this sprawl and maintain effective security without unnecessary complexity.
When you think of a scammer, you probably picture someone trying to deceive others for personal gain. While that’s usually true, there's another type of individual worth mentioning: those who scam the scammers. Enter Kitboga, a content creator and self-described "scam baiter" who has made it his mission to turn the tables on these cybercriminals.
Passwords have long been one of the central pillars of account security on the Internet. Combined with a username, they make up the foundation of most login systems. Because of this, they are a hot commodity for hackers who want to steal credentials and infiltrate accounts or networks. In recent years, however, other security measures have exposed the weakness of poor passwords for security, leading to the adoption of other measures.
Unfortunately, cyberattacks will only continue in the weeks, months, and years to come, making it increasingly essential that businesses have access to cybersecurity expertise. Even more unfortunately, professionals with this level of expertise are becoming harder to find. Globally, we’re short almost four million people, and those we have are prone to make mistakes in their first few years. This comes from a report by Kaspersky, entitled “The Portrait of Modern Information Security Professional,” Let’s review what the cybersecurity developer found and what we can take away from these findings.
It can be too easy to look at ransomware as a business problem. After all, it attacks businesses, locking down their data for ransom, often selling it or spreading it, and sometimes altering it for the business if returning it at all. It can be too easy to overlook another impacted target in all the mess.
What happens to the people whose data a business has collected and uses?
There are many parts of running a business where you cannot be too careful, one of which is the realm of cybersecurity. Many of the preventative measures you can implement aim to keep issues from making their way to your infrastructure in the first place, which makes sense from an operational standpoint. With an endpoint detection and response solution—or EDR—you’ll take an important step toward keeping most threats off your infrastructure.
We’ve spent the last few weeks discussing ransomware's impacts on different subsets. First, we discussed how a ransomware attack impacts the customers of the infected business, and then we touched on the infected business itself. To end, we want to touch on ransomware's impacts on society, specifically regarding economic health and geopolitical security, known as third-order harms.
Have you ever heard of the “man-in-the-middle” attack or MitM? It’s a situation where your data is stolen by an onlooker who situates themselves in the right place at the right time. Data interception is a very real thing that your business should be prepared to fight against. Let’s discuss some strategies you can use to counter these sneaky attacks.
On Wednesday, April 10, 2024, Apple deemed it necessary to send a rare alert to certain users via email, spread out across 92 nations. As Apple’s website states, these threat notifications “are designed to inform and assist users who may have been individually targeted by mercenary spyware attacks.” Let’s review these attacks so we all understand this threat better.